7 Proven Automation Examples in 2025 (From Dark Factories to AI Chatbots)
Automation is the use of technology that aims to make production more efficient by reducing human intervention in repetitive tasks.
It includes various technologies such as robotics, industrial machines, control systems, and AI and machine learning to perform tasks that were traditionally done by humans.
Automation seeks to improve productivity, accuracy, and safety by minimizing human involvement in repetitive, dangerous, or highly precise tasks.
The most developed use case of automation is the industrial production and manufacturing sectors that require lots of repetitive, dangerous, and noncomplex human labor. It increases efficiency, reduces costs, and maintains a standard and consistent product quality.
Automation systems can operate continuously without fatigue and can collect data to monitor equipment health and optimize processes.
One example of automation is Foxconn, Apple supplier, which replaced 60,000 factory workers with robots in 2016.
Automation Examples in Real Life
1. China's Dark Factories
Xiaomi’s fully automated smartphone factory in Changping, China, produces approximately one smartphone every 3 seconds without human intervention.
The automation structure combines AI-driven robotics, IoT sensors, and machine learning for assembly, quality control, predictive maintenance, and smart logistics.
The factory runs 24/7 without lights or human presence, using automated guided vehicles and robotic arms for manufacturing and material handling.
It dramatically increases efficiency and precision, reduces labor costs, minimizes human error, lowers energy consumption, and allows nonstop production. It also enables real-time quality monitoring and predictive maintenance to reduce downtime.
Wall Street Journal. China’s Dark Factories: So Automated, They Don't Need Lights. YouTube video.
2. Amazon’s Automated Warehouses
As of 2025, Amazon has over 1 million robots operating in its warehouses. America’s online retailer uses robots alongside human workers to automate sorting, packing, and shipping in their fulfillment centers globally.
Autonomous mobile robots transport shelves of products to human pickers, who then pack and dispatch orders. AI algorithms optimize inventory location, route planning, and order fulfillment prioritization.
Robots speed up order processing, reduce human walking time, improve workspace organization, increase throughput, and scale operations during peak demand like Black Friday and Cyber Monday.
Amazon News. Meet Amazon's First Fully Autonomous Mobile Robot. YouTube video.
3. Foxconn’s Kunshan Factory Automation
Apple supplier Foxconn replaced 60,000 workers with robots in its Kunshan electronic manufacturing plant in China.
They automated the production by letting robots perform assembly line work for electronics manufacturing, with AI systems monitoring production quality and managing logistics internally.
As a result, it dramatically cut the labor costs, increased production consistency, and output capacity.
4. Gree Electric Appliances' 5.5G Lights-Out Factory
Gree transformed its Gaolan factory into a 5.5G-enabled fully automated factory with no lights, running exclusively on robots and AI systems for manufacturing.
The company utilized advanced telecommunications for real-time data sharing and coordination between robots, sensors, and production units. This factory runs continuously with increased production efficiency by 86%.
The system works with high production efficiency, ultra-low downtime, energy savings, and improved product quality due to intelligent monitoring.
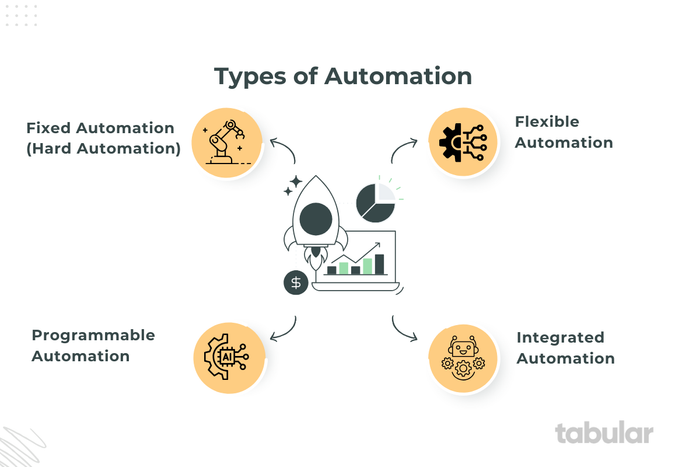
4 Main Types of Automation
- Fixed Automation (Hard Automation): Designed for high-volume production, it uses specialized equipment to perform a specific repetitive task. It offers high efficiency and low unit costs but lacks flexibility and is costly to set up and modify. Examples include mechanized assembly lines and conveyor belts.
- Programmable Automation: This type allows reprogramming of equipment to handle different tasks, suitable for batch production. It uses programmable logic controllers (PLCs), industrial robots, and CNC machines. It is more flexible than fixed automation but slower and requires reprogramming for each new task.
- Flexible Automation (Soft Automation): Offers high adaptability and quick changeovers between tasks without significant downtime, ideal for varied product production. Examples are robot arms in manufacturing that can perform diverse tasks. It is complex and requires skilled technicians.
- Integrated Automation: Combines various automation types into a single system to automate entire production processes with minimal human involvement. It includes advanced technologies like AI and IoT, used in industries like pharmaceuticals and large-scale manufacturing. It improves efficiency but has high costs and complex integration.
5 main benefits of automation in production
- Continuous 24/7 operation without fatigue or breaks
- Lower labor and operational costs
- Increased production precision and quality
- Reduced energy consumption (no lighting/heating needed)
- Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven adjustments
5 disadvantages of automation in production
- High initial cost and investment
- Risk of system downtimes and technical challenges
- High maintenance cost and overreliance on technical products
- Reduced human interaction and customer experience
Typical Costs and ROI for Automation
Typical costs for automation projects vary widely depending on complexity, scale, and technology involved. For industrial automation:
Initial capital investment can range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars.
For example,
- AI-powered systems may cost from $100,000 to over $1 million.
- Machine vision systems can cost between $25,000 to $250,000, while automated test equipment varies from $50,000 to $500,000 or more.
- Other expenses include consulting/planning (5-15%), installation (10-25%), testing (5-10%), maintenance (3-8% annually), and training (1-3% annually) of the total investment.
- Operational costs include maintenance, energy consumption, software updates, and skilled labor.
Regarding ROI (Return on Investment):
ROI = (Net Profit from Investment / Cost of Investment) * 100. Benefits of automation in include cost savings from labor reduction, error reduction, and additional revenue.
Typical payback periods for automation investments range from 12 to 36 months, depending on the sector and system complexity. Some projects see ROI within 6 months to 5 years.
ROI percentages can vary widely but automation projects often see 15-50% ROI in the first year, with some robotic process automation reaching 30%-200% ROI.
On average, companies make $5.44 in revenue for every $1 spent on marketing automation, with the ROI of 544%. About 76% of companies see ROI within one year, and 12% start seeing it in less than a month. Email marketing above other channels yields a remarkable $36 return for every $1 spent, equating to a 3600% ROI.
With Tabular's drag and drop email template builder, you can create html email templates for successful email marketing automations in seconds, for free!
Examples of Automation in 2025
- AI-Powered Automation: Automates administrative tasks, patient data management in healthcare, fraud detection, resource allocation, and compliance management in manufacturing. AI systems like IBM Watson and ChatGPT handle complex decision-making, document processing, and communication unification
- Task Automation: Automates repetitive, routine tasks such as scheduling social media posts, email follow-ups, and smart home controls (e.g., lights turning off when leaving a house). Platforms like IFTTT enable easy workflow automation for everyday tasks.
- Human-Cobot Collaboration: Collaborative robots (cobots) work safely alongside humans to automate routine tasks while allowing humans to focus on strategic work, enhancing productivity and job satisfaction.
- Plug & Produce Solutions: Modular, quick-to-deploy automation systems that enable fast integration in production lines, well-suited for small and medium-sized businesses aiming for fast ROI.
- Warehouse Automation: Robotics, AI, and machine learning optimize capacity planning, inventory control, demand prediction, and maintenance scheduling, making warehouse operations more efficient and responsive.
- Embodied AI & Self-Aware Machines: AI integrated into physical robots that understand and adapt to their surroundings, opening new frontiers in manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.
Examples of Automation in Business
- AI-Powered Workflow Automation: Automated process approvals, record management, and compliance in industries like energy and finance, replacing manual code-heavy workflows with no-code AI platforms.
- Fraud Detection & Financial Automation: Real-time transaction monitoring, automated loan processing, and compliance management using AI to reduce risk and improve processing speed.
- Healthcare Automation: Digitizing patient details, automating administrative tasks, and streamlining operation notes to let clinicians focus more on patient care.
- AI in Recruiting: Automating CV screening, candidate matching, and speeding up hiring processes while improving quality of candidates.
- AI-Generated Reporting: Automating data collection, analysis, and generating reports for customer success, product teams, and educators to improve decision making.
- Invoice Capture & Processing: Automating invoice extraction, matching financial data, and payment approvals to improve finance department efficiency.
- Legal Document Automation: Drafting contracts, validating compliance, and streamlining legal approvals through AI workflows.
- Customer Support Automation: AI chatbots handling common queries and routing issues reducing support tickets and enhancing customer experience.
- Security Automation: Automated compliance checks, AI-driven threat detection, and built-in security layers to reduce business risks.
- Business Process Automation Trends: AI agents replacing traditional bots, predictive automation, autonomous workflows, and privacy-first architectures shaping 2025 automation strategies.
Examples of Marketing Automation in 2025
- Customer Onboarding: Automated welcome emails, product tutorials, and support resources to make a positive first impression, improve satisfaction, and reduce support workload. (Spotify uses this to greet and inform new subscribers).
- Lead Scoring: Automation to score leads based on interactions like website visits and email opens, enabling sales teams to focus on the most promising prospects.
- Cold Outreach: Automating personalized emails to prospects who haven't interacted with the brand yet, increasing reach and lead generation efficiently.
- A/B Testing Email Campaigns: Automated A/B testing of subject lines, content, and timing to identify what engages audiences best and optimize future emails
- Reducing Customer Wait Times: Virtual assistants and chatbots that handle common customer inquiries, improving responsiveness and reducing support call volumes.
- AI-Driven Campaign Optimization: AI spots trending keywords, underperforming segments, and unusual user behavior to optimize campaigns across multiple marketing channels.
- Automated Lead Capture and Data Entry: Syncing lead data across marketing tools and CRM platforms automatically to maintain data consistency and trigger relevant campaigns.
- AI Chatbots for Lead Qualification: Automating early conversations to qualify leads, schedule demos, and send nurturing content without manual effort.
Popular tools supporting marketing automation include Tabular for creating personalized emails, HubSpot for all-in-one marketing, sales, and service automation, and Zapier for workflow integrations
Automation Use Cases in 2025
1. AI-Powered Chatbots for Customer Support
Deploy AI chatbots on your website or app to handle common customer queries like order status or FAQs.
Use platforms like LiveChat or Intercom with custom llm models, integrating with CRM for personalized responses. Train staff for chatbot management and direct complex issues to humans.
Pros:
- Reducing wait times and operational costs
- 24/7 availability
Costs:
- Reduced customer satisfaction
- Limited in handling complex or emotional queries
2. Invoice Processing Automation
Implement robotic process automation (RPA) tools to extract invoice data, validate it against purchase orders, and automate approval workflows. Integrate with ERP or accounting systems.
Pros:
- Reduces errors and manual data entry
- Speeds up payment cycles
- Lowers processing costs by up to 60%
Cons:
- High initial setup and integration costs
- Dependence on system accuracy
- May not handle highly irregular or non-standard invoices
3. Email Marketing Automation
Set up automated email sequences using platforms like Mailchimp or HubSpot triggered by user behavior (e.g., sign-ups, purchases). Create html emails using tools like Tabular to create personalized emails. Use A/B testing and personalization based on analytics. Continuously monitor key metrics and optimize workflows.
Pros:
- Improves engagement with personalized, behavior-triggered campaigns
- Increases ROI (25–40%) compared to manual campaigns
- Saves time on repetitive tasks like sending follow-ups
Cons:
- Risk of over-automation, making emails feel impersonal or spammy
- Requires good data hygiene; poor segmentation reduces effectiveness
- Can hurt brand reputation if workflows misfire (e.g., wrong triggers, duplicate emails)
- Compliance challenges (GDPR, CAN-SPAM) if not managed properly
4. Predictive Analytics for Inventory Management
Use AI tools that analyze historical sales data and external factors to forecast demand. Integrate predictive models with inventory and supply chain systems to automate stock replenishment decisions. Pilot with high-value or fast-moving products.
Pros:
- Reduces stockouts and overstock situations
- Improves cash flow by optimizing inventory levels
- Aligns supply with real demand, increasing profitability
- Supports proactive decision-making in supply chain management
Cons:
- Requires large volumes of accurate, clean data to work effectively
- Forecasting errors can lead to costly supply chain disruptions
5. Robotic Process Automation in Data Entry
Identify repetitive, rule-based tasks like entering customer data from forms into CRM. Deploy RPA bots to perform this automatically with minimal human supervision. Continuously monitor for exceptions and refine the bot scripts.
Pros:
- Eliminates human error in repetitive, rule-based tasks
- Saves employees’ time for higher-value activities
- Increases speed and consistency of data processing
- Scales easily for high-volume workflows
Cons:
- Limited to structured, rule-based processes (not flexible for exceptions)
- Requires continuous monitoring and script maintenance
- Implementation can be costly relative to smaller organizations
- Risk of job displacement or resistance from staff
Final Words
Automation has become a transformative force across industries, shaping how businesses operate, produce, and interact with customers. We now started to see fully automated factories like Xiaomi’s dark factory and Foxconn’s Kunshan plant. AI-driven business operations and marketing processes have the potential to increase efficiency, precision, and scalability while reducing costs and human fatigue.
However, it also comes with challenges, including high upfront costs, technical complexity, maintenance requirements, and potential impacts on human employment and customer experience. Even though it offers great value, automated systems can also be deadly for production, as human labor is easily replaceable and costs less compared to the whole system, and most businesses are not capable of affording the cost of any malfunction. As technology continues to advance, best practice is to balance automation with human oversight, using AI and robotics to handle repetitive or data-intensive tasks while allowing humans to focus on strategic, creative, and interpersonal work.
Automation is not about replacing human effort; it is about increasing efficiency, and if you are interested in efficient workflows, Tabular is just the email builder for your business.
Tabular is an email design software that enables users to create html emails that are compatible in all clients just by dragging and dropping design elements, no coding at all. For advanced users, you can also customize code, utilize Tabular’s advanced personalization, and collaboration features for your marketing campaigns.